Single-source Shortest Path (Weighted)
Finding shortest paths in a graph with weighted edges is algorithmically harder than in an unweighted graph because even after you find a path to a vertex T, you cannot be certain that it is a shortest path. If edge weights are always positive, then you must keep trying until you have considered every in-edge to T. If edge weights can be negative, then it’s even harder. You must consider all possible paths.
A classic application for weighted shortest path is finding the shortest travel route to get from A to B. (Think of route planning "GPS" apps.) In general, any application where you are looking for the cheapest route is a possible fit.
Specifications
The shortest path algorithm can be optimized if we know all the weights are nonnegative. If there can be negative weights, then sometimes a longer path will have a lower cumulative weight. Therefore, we have two versions of this algorithm
tg_shortest_ss_pos_wt (VERTEX source, SET<STRING> v_type, SET<STRING> e_type,
STRING wt_attr, STRING wt_type, INT output_limit = -1, BOOL print_accum = TRUE,
STRING result_attr = "", STRING file_path = "", BOOL display_edges = FALSE)tg_shortest_ss_any_wt (VERTEX source, SET<STRING> v_type, SET<STRING> e_type,
STRING wt_attr, STRING wt_type, INT output_limit = -1, BOOL print_accum = TRUE,
STRING result_attr = "", STRING file_path = "", BOOL display_edges = FALSE)| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
Result |
Computes a shortest distance (INT) and shortest path (STRING) from vertex source to each other vertex. |
Input Parameters |
|
Result Size |
V = number of vertices |
Time Complexity |
O(V*E), V = number of vertices, E = number of edges |
Graph Types |
Directed or Undirected edges, Weighted edges |
|
The shortest_path_any_wt query is an implementation of the Bellman-Ford algorithm. If there is more than one path with the same total weight, the algorithm returns one of them. Currently, shortest_path_pos_wt also uses Bellman-Ford. The well-known Dijsktra’s algorithm is designed for serial computation and cannot work with GSQL’s parallel processing. |
Example
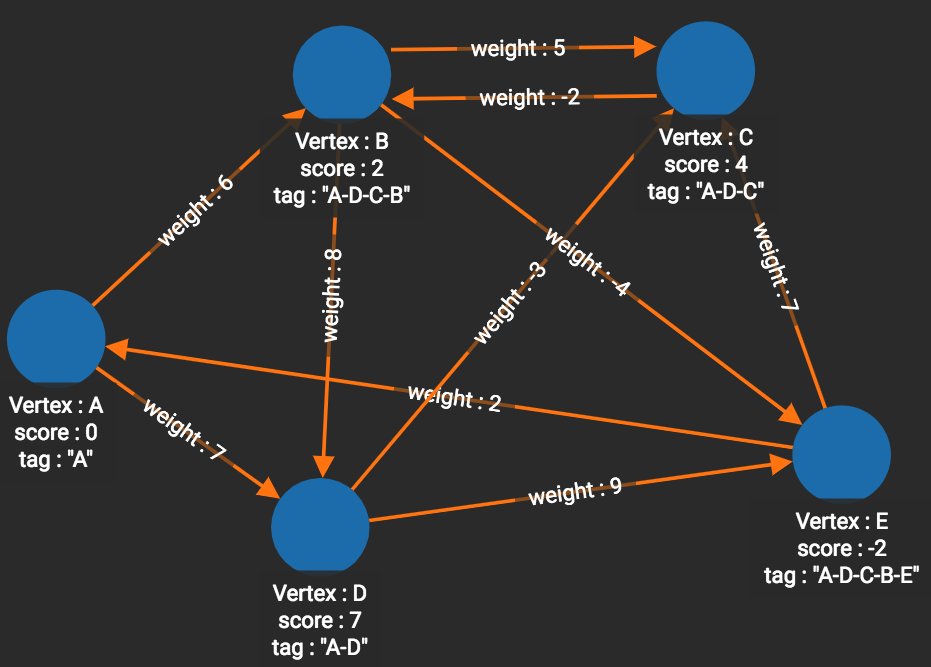
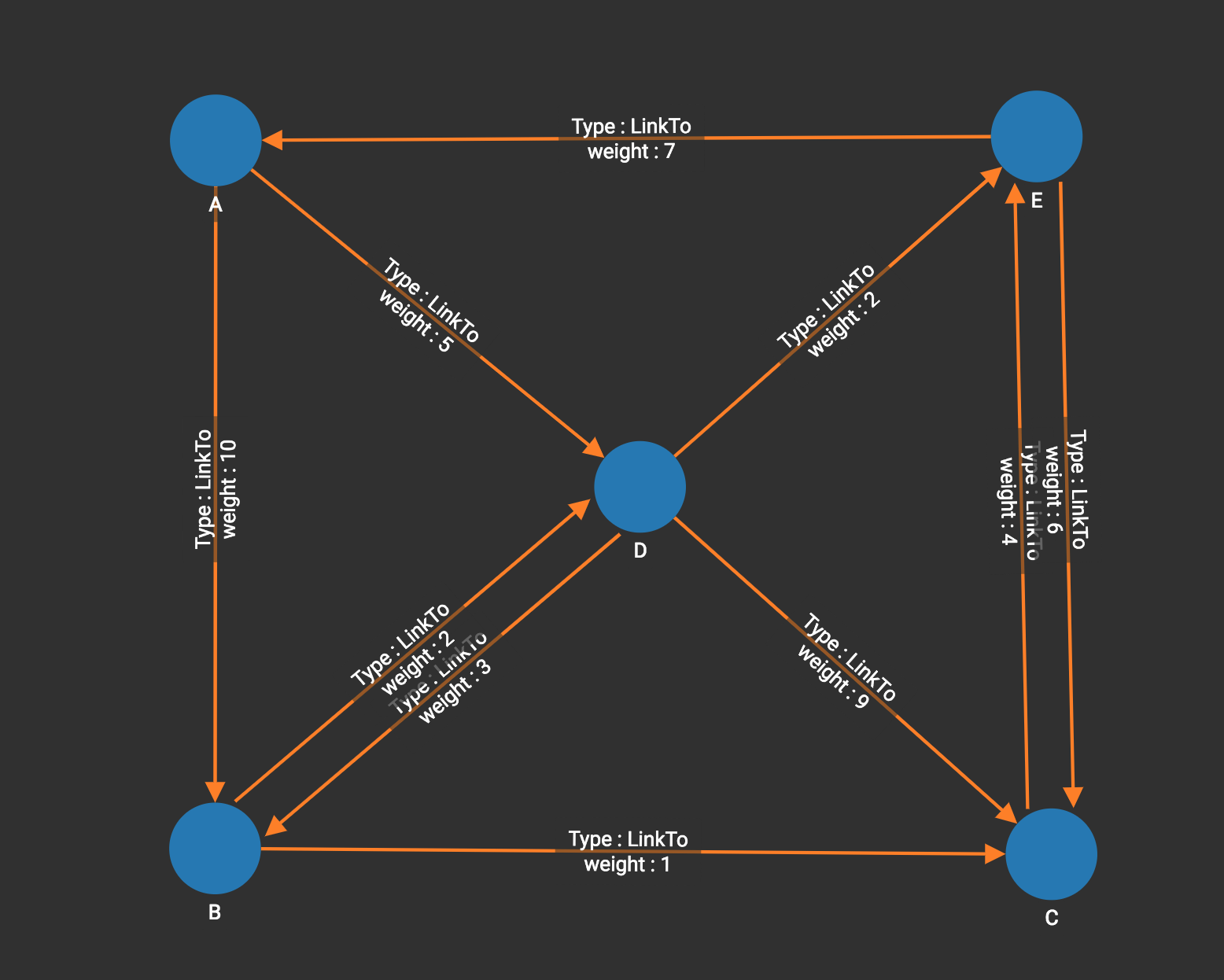
The graph below has only positive edge weights. Using vertex A as the source vertex, the algorithm discovers that the shortest weighted path from A to B is A-D-B, with distance 8. The shortest weighted path from A to C is A-D-B-C with distance 9.
[
{
"ResultSet": [
{
"v_id": "B",
"v_type": "Node",
"attributes": {
"ResultSet.@dis": 8,
"ResultSet.@path": [
"D",
"B"
]
}
},
{
"v_id": "A",
"v_type": "Node",
"attributes": {
"ResultSet.@dis": 0,
"ResultSet.@path": []
}
},
{
"v_id": "C",
"v_type": "Node",
"attributes": {
"ResultSet.@dis": 9,
"ResultSet.@path": [
"D",
"B",
"C"
]
}
},
{
"v_id": "E",
"v_type": "Node",
"attributes": {
"ResultSet.@dis": 7,
"ResultSet.@path": [
"D",
"E"
]
}
},
{
"v_id": "D",
"v_type": "Node",
"attributes": {
"ResultSet.@dis": 5,
"ResultSet.@path": [
"D"
]
}
}
]
}
]The graph below has both positive and negative edge weights. Using vertex A as the source vertex, the algorithm discovers that the shortest weighted path from A to E is A-D-C-B-E, with a cumulative score of 7 - 3 - 2 - 4 = -2.